Dinosaurs ruled the world of our planet for 130 million years - 100 times longer than the human race exists on Earth. Life on the planet was in mortal danger. Flying reptiles disappeared. In the oceans, waterfowl reptiles, like mollusks and starfish, became extinct. Even the majority of small animals - plankton - have died out.
Why did dinosaurs die out?
Nobody knows for sure. But there are so many theories. Most of them suggest that there have been some major changes in the climate of our planet that have damaged many living organisms, not just dinosaurs. The latest and most popular theory claims that dinosaurs and other animal species died out due to one terrible universal catastrophe: 65 million years ago, the Earth collided with an asteroid, and at the same time there was a terrible force explosion.
Interesting fact: in addition to dinosaurs, 65 million years ago, flying reptiles and a large number of marine inhabitants died out.
Examining clay deposits in the layers of the earth's crust, dated as deposited 65 million years ago, scientists found a large content of iridium in these rocks. Iridium is rarely found on Earth, since during the formation of our planet, iridium as a heavy element plunged deep underground and is located mainly near the earth’s core.

Iridium enters the Earth only from space, when meteorites and asteroids fall from the sky.Scientists have found iridium in ancient clay deposits around the world. Here's their conclusion: iridium fell out of a cloud of dust that was thrown into the atmosphere when an asteroid collided with the Earth. Here is what could happen.
Dinosaur extinction hypothesis

An asteroid with a diameter of 10 or more kilometers flew from space into the Earth’s atmosphere at a speed of at least 100,000 kilometers per hour. Crashing into the Earth, he formed a crater with a diameter of 160 kilometers. Tons of crumbled rocks and soil (a mixture of rock asteroid and Earth) from the explosion soared high into the sky. From passing through the atmosphere of a fireball and an explosion in the atmosphere, hurricanes arose, which smashed dust soaring into the sky throughout the Earth. A huge dust cloud clouded the sky. The sun went dark and day became night. The gloom lasted for months. The average daily temperature dropped from plus 19 to minus 10 degrees Celsius. The mass death of plants and animals caught in the gloom and cold began.
Following the herbivores, the predators that ate the herbivores began to die out. In the end, the cloud fell to the ground, leaving a memory of itself in the form of a large admixture of iridium. Many scientists, however, are skeptical of this theory. Why, then, they ask, did the birds, crocodiles, turtles, snakes and most mammals survive, and insects, mollusks, ocean fish, and many plants survived. This theory is doubtful also because the extinction of the dinosaurs was very slow - over millions of years, and not during one gigantic cataclysm.
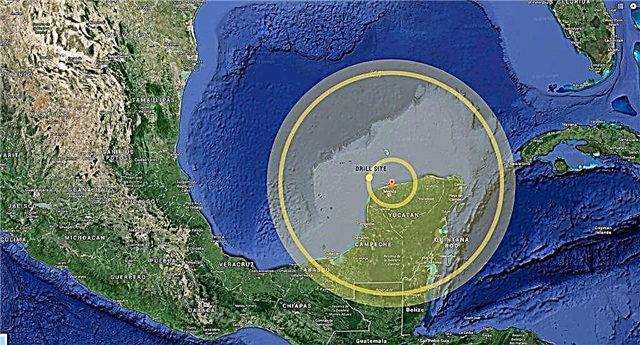
Interesting fact: The asteroid that caused the global catastrophe and led to the extinction of the dinosaurs may have collided with Earth in the area of the Yucatan Peninsula.
There are scientists who claim that iridium could mix with sedimentary rocks during eruptions of numerous volcanoes, when lava erupts from deep earth bowels. Volcanic eruptions could throw so much ash into the atmosphere that it would block the sun no worse than dust from an asteroid explosion. This could also be the cause of the extinction of the dinosaurs.
Confirmation of the asteroid hypothesis of the extinction of dinosaurs
The only advantage of an asteroid theory is that it can be verified. Scientists were looking for a suitable crater. Looking at space photographs of Mexico, they discovered a semicircular chain of lakes. These lakes on the Yucatan Peninsula can border the edges of a giant crater buried under a mile layer of stones. In 1992, scientists obtained rock samples from the depths of a proposed crater when the Mexican National Oil Company carried out drilling operations at this site. After dating the samples, scientists found that the crater is indeed about 65 million years old.
At the same time, scientists who studied fossils of leaves from rock samples, which are 65 million years old, found that these leaves were very affected by severe frost. The leaf development stage showed that they froze in June. Fossilized leaf debris is additional evidence that rock debris and dust raised in the air from a large explosion could suddenly lower air temperature.Scientists, however, argue that this event, even if it really took place, could be the cause of the extinction of dinosaurs.