Big Bang. Especially frightening, if ever you asked yourself very difficult questions about the universe.
For example, if the Universe is all that is, then how did it begin? And what happened before that? If space is not infinite, then what is beyond it? And in what should this something actually be placed? How can one understand the word "endlessly"?
These things are hard to understand. Moreover, when you start to think about it, an eerie sensation of something majestic - terrible, encompasses. But questions about the universe are one of the most important questions that humanity has been asking itself over the course of its history.
What was the beginning of the existence of the universe?
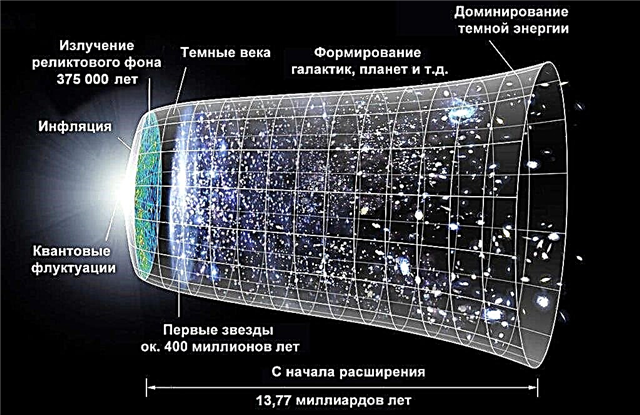
Most scientists are convinced that the beginning of the existence of the Universe was laid by a grandiose big explosion of matter that occurred about 15 billion years ago. For many years, most scientists shared the hypothesis that the beginning of the Universe was laid by a grand explosion, which scientists jokingly dubbed the “Big Bang”. In their opinion, all matter and all space, which is now represented by billions and millions of galaxies and stars, 15 billion years ago fit in a meager space the size of which does not exceed a few words in this sentence.
How was the universe formed?
Scientists believe that 15 billion years ago, this small volume exploded into the smallest particles smaller than atoms, laying the foundation for the existence of the Universe.Initially, it was a nebula of small particles. Later, when these particles joined together, atoms formed. Out of atoms, star galaxies formed. Since this Big Bang, the Universe continues to expand, like a balloon.
Doubts about the Big Bang Theory
But over the past few years, scientists studying the structure of the universe have made some unexpected discoveries. Some of them question the Big Bang theory. What can you do, our world does not always correspond to our convenient ideas about him.
Substance distribution in the Big Bang
One problem is the way matter is distributed throughout the universe. When an object explodes, its contents scatter evenly in all directions. In other words, if matter was initially compressed in a small volume, and then exploded, then the matter should have been evenly distributed throughout the universe.
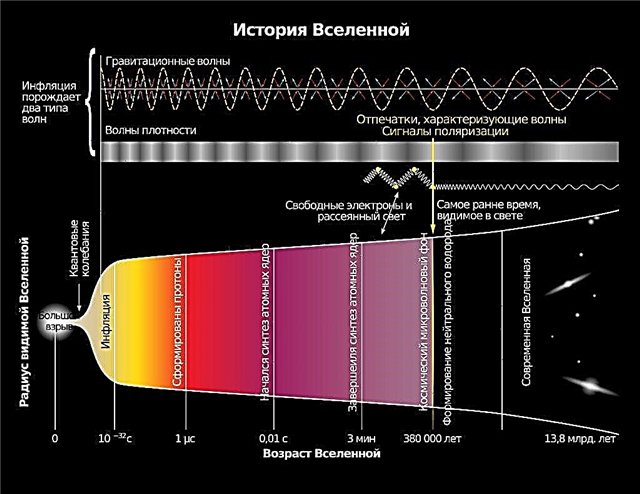
The reality, however, is very different from what is expected. We live in a very unevenly filled Universe. When looking into space, the gaze appears separate clumps of matter remote from each other. Huge galaxies are scattered here and there in outer space. Between the galaxies stretches huge sections of empty emptiness. At a higher level, galaxies are grouped into clusters - clusters, and these last - in mega clusters. Be that as it may, scientists have not yet come to an agreement on how and why precisely such structures were formed. In addition, a new, even more serious problem recently arose with everything.
Interesting fact: according to the Big Bang theory: the Universe was once assembled in a volume not exceeding the size of several words in this sentence.
Chains of galaxies
Using the latest technological advances, including telescopes placed in high Earth orbit, scientists were able to discover even more mysterious structures in space - long chains of galaxies. This is another contradiction in the beautiful theory of the even distribution of matter in the Universe as a result of the Big Bang.
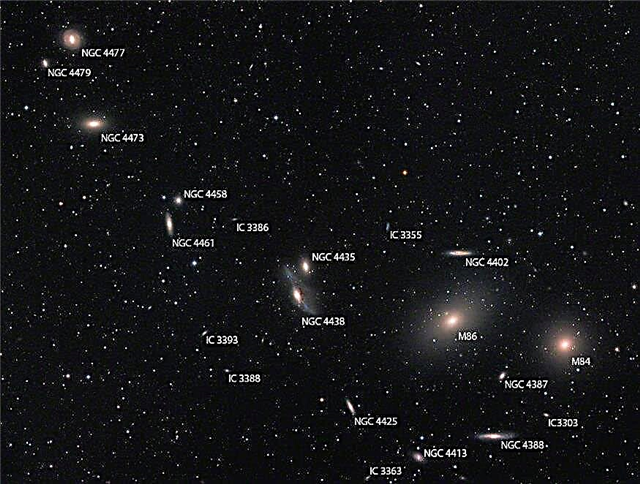

To solve these puzzles, scientists are trying to modify the Big Bang theory, adapting it to new facts. The best way is this. The force of gravity causes the parts of the matter to group together, to accumulate together, while small clusters tend to constantly increase in size, forming huge clouds resembling a layer cake in shape. Its layers are composed of hydrogen and helium gases. Under the influence of gravity, clouds are attracted to each other and primary clusters of stars - galaxies - are formed. After this, individual clouds-galaxies under the influence of attractive forces again form clusters (clusters of galaxies).
Sustainability Theory
Some scientists have not completely abandoned the Big Bang theory. They are working to revive earlier theories of creation, such as the Theory of Steady State. The main postulate of this theory is that the Universe has always been and will be forever. According to this model, there was no beginning of the Universe, and there will be no end either. Over time, matter is constantly being recreated, forming new star galaxies.